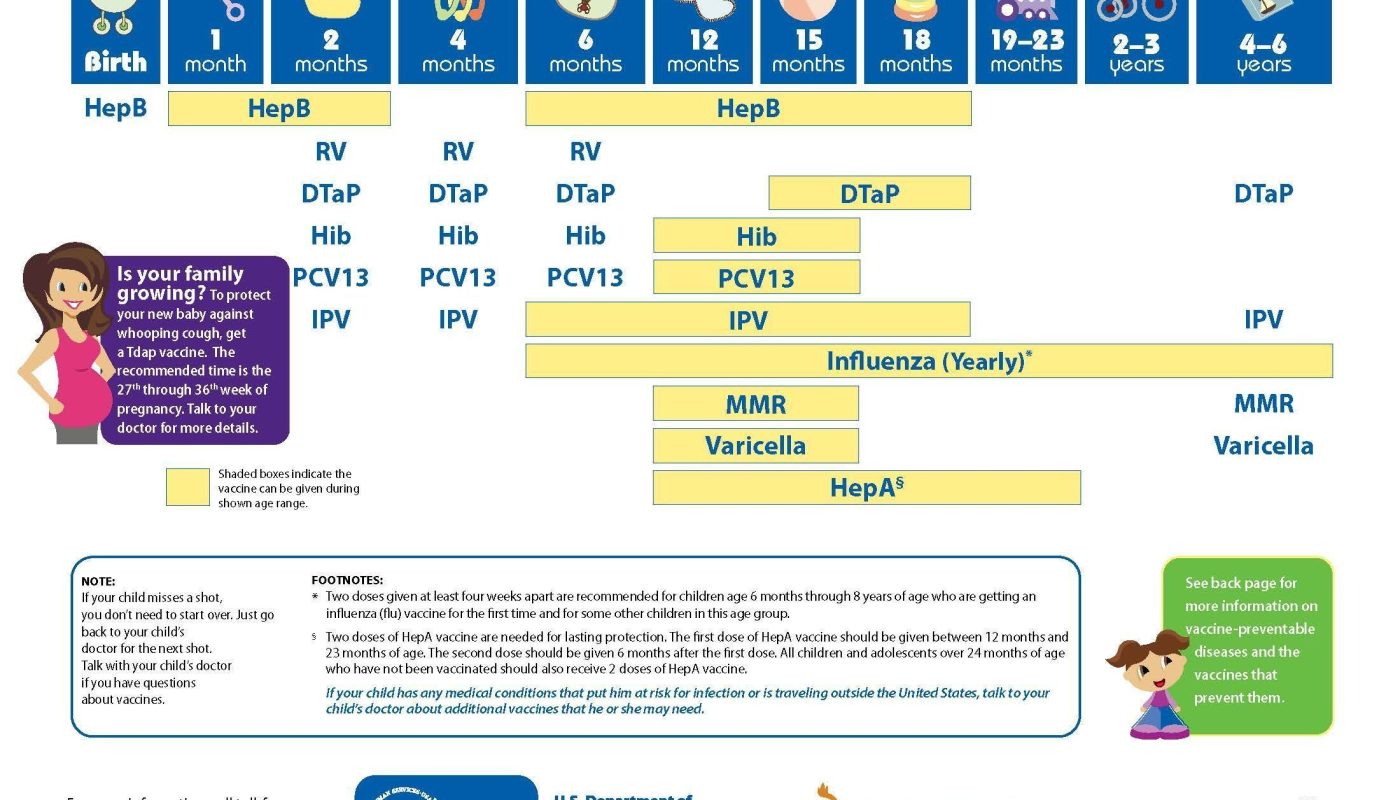
Childhood immunization plays a crucial role in protecting children from various diseases and promoting their overall health. Vaccines are designed to stimulate the immune system to develop immunity to specific pathogens, preventing the occurrence of potentially severe illnesses. This article will provide an overview of the recommended immunization schedule for a healthy childhood.
Why Immunization is Important
Immunization is important as it safeguards children against a range of infectious diseases that can have long-lasting and adverse effects on their health. Vaccines have proven to be extremely effective in preventing diseases such as measles, polio, hepatitis, influenza, and more. Through immunization, we can achieve herd immunity, protecting not only the vaccinated child but also vulnerable individuals who are unable to receive vaccines, such as newborns or individuals with compromised immune systems.
Immunization Schedule
The immunization schedule recommended by healthcare professionals and organizations may vary slightly, depending on factors such as geographic location and available vaccines. However, the following is a general guideline for childhood immunization:
Birth to 2 Months
Hepatitis B (HepB) vaccine
2 Months
Diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (DTaP) vaccine
Hepatitis B (HepB) vaccine
Inactivated poliovirus (IPV) vaccine
Pneumococcal conjugate (PCV13) vaccine
Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccine
4 Months
Diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (DTaP) vaccine
Hepatitis B (HepB) vaccine
Inactivated poliovirus (IPV) vaccine
Pneumococcal conjugate (PCV13) vaccine
Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccine
6 Months
Diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (DTaP) vaccine
Hepatitis B (HepB) vaccine
Inactivated poliovirus (IPV) vaccine
Pneumococcal conjugate (PCV13) vaccine
12-15 Months
Hepatitis A (HepA) vaccine
Measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine
Varicella (chickenpox) vaccine
18 Months
Diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (DTaP) vaccine
Hepatitis A (HepA) vaccine
Inactivated poliovirus (IPV) vaccine
4-6 Years
Diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (DTaP) vaccine
Poliomyelitis (IPV) vaccine
Measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine
Varicella (chickenpox) vaccine
Note: This is a general immunization schedule, and it is essential to consult with your pediatrician or healthcare provider to ensure your child receives the appropriate vaccines at the recommended times.
Benefits and Safety of Immunization
Immunization offers several benefits to children and society as a whole:
Protection against diseases: Vaccines protect children from serious, potentially life-threatening diseases.
Prevents complications: Immunization reduces the risk of severe complications, including hospitalization and long-term disabilities.
Herd immunity: By vaccinating a significant portion of the population, herd immunity can be achieved, reducing the overall transmission of diseases within communities.
Cost-effective: Preventing diseases through vaccines is more cost-effective than treating illnesses and their consequences.
Vaccines undergo extensive testing before they are approved and distributed. They are carefully evaluated for safety and efficacy by regulatory agencies and medical experts. Serious side effects are extremely rare, and the benefits of immunization far outweigh the minimal risks involved.
Conclusion
Following the recommended immunization schedule for a healthy childhood is vital to protect children from preventable diseases and promote their overall well-being. Vaccination provides a safe and effective way to strengthen their immune systems and reduce the risk of severe illnesses. It is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized guidance and ensure timely administration of vaccines. Let us work together to ensure a healthier future for our children.